3D Scanning
3D Digitization
3D scanning allows control geometry exhaustively or generate a CAD from a pre-existing piece.
This technology is used from the scanning of small or large pieces, to the digitization of civil engineering buildings or even pieces of cultural heritage.
We scan the part or area to then create a polygonal model, which after being treated, can be used to make 3D prints of it, manufacturing, creating a virtual parts stock warehouse and dimensional quality control.
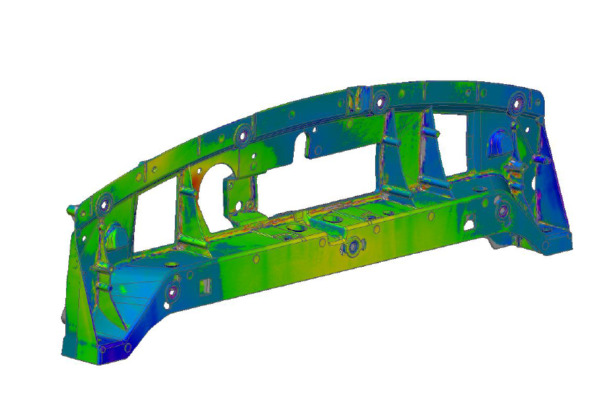
Applications
- Dimensional inspection of parts comparing against the CAD. We create a color map, so that quality control is simplified and much more intuitive.
- Surface scanning of the part or component, we carry out subsequent cloning using additive manufacturing.
Advantages
- Reduce production times and costs identifying problems in the design or manufacturing before the physical prototype is produced.
- Improve product quality creating accurate virtual models.
- Accelerate innovation creating virtual prototypes and exploring different design options.
- Facilitates additive manufacturing allowing rapid and accurate creation of prototypes and production parts in small quantities.
- Helps create complex models and its simulation to analyze dimensions, tolerances, deformations...
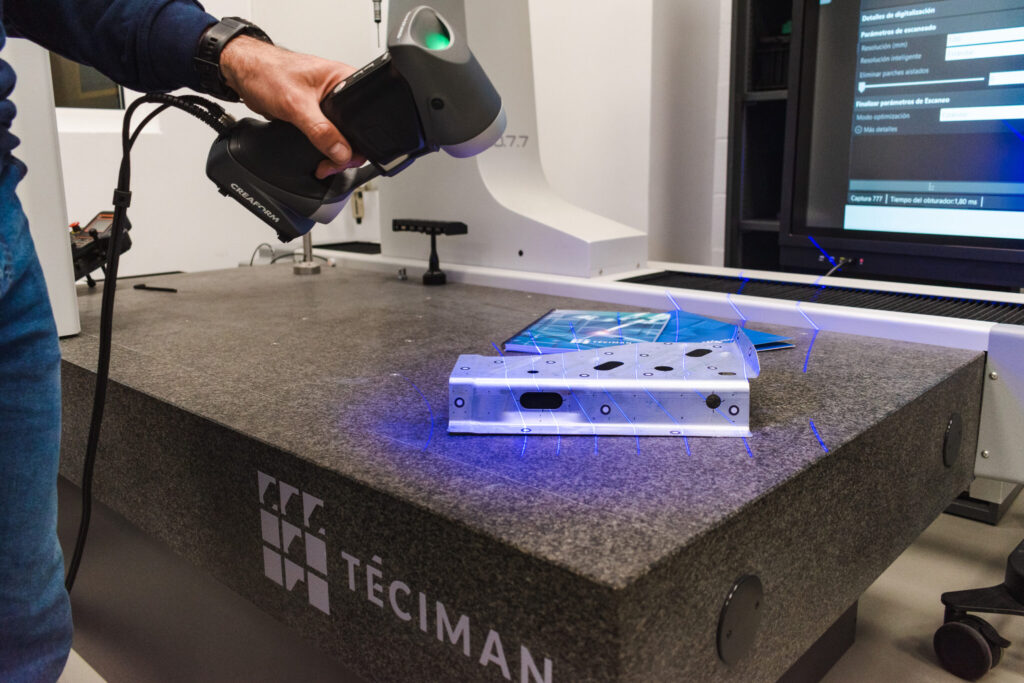
Reverse Engineering
It is the best solution when We do not have a previous CAD or it is insufficient.
Starting from the point cloud obtained by scanning, we create a polygonal model in “stl” format. This format includes the skin of the piece or surface.
To generate the solid 3D model of the part (similar to one done using Solidworks, Inventor, Catia…) we support ourselves in the area of Téciman Design and Simulation. Using specific software, CAD modeling is carried out, obtaining 3D. This model can be modified and worked using any CAD/CAM software for subsequent manufacturing.

Applications
- Create CAD models of existing parts or components: useful for the manufacture of spare parts or for improving the design of a component.
- Analyze and improve the design of a component: Obtaining detailed information about its design and operation helps identify potential problems and improve component design.
- Upgrade or replace obsolete parts not available on the market. Reverse engineering can be used to recreate these parts obtaining functional spare parts.
- Create tool models for the manufacture of related parts or components.
Advantages
- Allows creation of accurate CAD models without the need to have the original plans.
- Save time and costs, improving the existing design instead of creating a new one from scratch.
- Facilitates the manufacturing of custom parts, which is useful for repairing old equipment.
- Enables the identification of problems and failures in its design and operation, helping to improve it.
- Allows updating of old equipment to recreate obsolete parts, extending their useful life and avoiding the need to replace all equipment.
BIM
The Building Information Modeling model allows us to manage the quality of the geometry of a building or ship in all its project phases, whether in its useful life or in the construction phase.
This system is based on the digitization and centralization of data and 3D CAD to improve the management of the building's geometry, better facing the changes that may occur in its structure.
By generating point clouds we can see how the different structural elements interact and preview the best solutions.
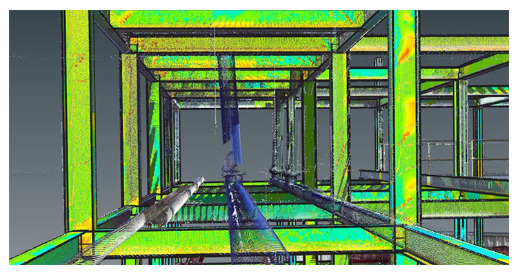
Applications
- Project planning and design: useful for creating accurate digital models of buildings and structures before they are built, organizing the different work cells.
- Collaboration on the project: BIM models can be shared between different design and construction teams, facilitating communication and coordination.
- Construction: Ensures that components and systems are built according to design specifications. And it helps in planning and coordinating work at the construction site.
- Maintenance and renovation: useful for planning and scheduling long-term maintenance and renovation of buildings and structures.
Advantages
- Improves design accuracy and efficiency.
- Reduces errors and construction costs: identifies problems before starting construction.
- Facilitates collaboration and communication between teams
- Efficient building management and maintenance: assists in management throughout the life cycle.
Big Surfaces
We have the ability to scan a building, industrial warehouse either hall with all its complexity. We capture the color and point cloud and compare it against the CAD.
Perfect for him sizing of new facilities in industrial warehouses, installation of new machinery, improvement of the layout of an industrial plant or simply to carry out a dimensional control of a building built or under construction.
It is also used in the measurement of large assemblies, systems or components, allowing their modeling or measurement.

Applications
- Inspection and quality control: Helps identify production problems and defects and verifies compliance with necessary quality standards.
- Design and prototyping: Creates accurate and detailed digital models.
- Maintenance and repair: useful for identifying problems and defects early.
Advantages
- More precision: Accurate measurements down to microns, detecting problems early.
- Greater efficiency: saving time and resources
- Detailed reports: Helps make informed decisions about production and performance.
- Flexibility: adaptable to various applications and needs in different industries and sectors.
Heritage and Art
Through the scanning And later digitization we capture the geometry and colors of any piece of art or heritage. From a statuette to a complete building.
With this technology we manage to carry out a timeless archive of the piece, ideal to have as a base prior to any restoration work.
It is also possible to perform a scan in order to create virtual visits.
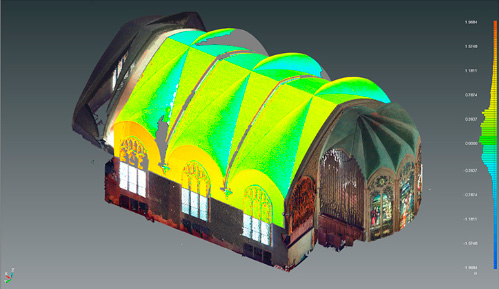
Applications
- Conservation and restoration: creates precise digital models to identify damage, deformations, and other problems that need to be corrected. 3D measurement is also used in the manufacturing of replacement parts and repair of objects.
- Digitization: of historical and cultural objects for their preservation. It allows you to create replicas as teaching tools and for display in virtual museums.
- Research and documentation: provides valuable information about the history, culture, materials and techniques used.
Advantages
- Provides precision and detail
- Help conserve and preserve historical and cultural objects
- It is flexible: can be used in statues, paintings, murals...
- Multiple applications: digitization, research, documentation and creation of digital models.